Features:
a. High-performance: The industrial-grade PoE + SFP fiber switch offers adaptive transmission rates of 10/100/1000Mbps, ensuring high-speed data transmission and meeting the bandwidth requirements of various application scenarios.
b.Energy-efficient: The SFP fiber switch actively powers devices via PoE, eradicating extra adapters and minimizing energy use.
It further incorporates EEE tech, automatically adjusting power output based on network load, thereby enhancing energy savings.
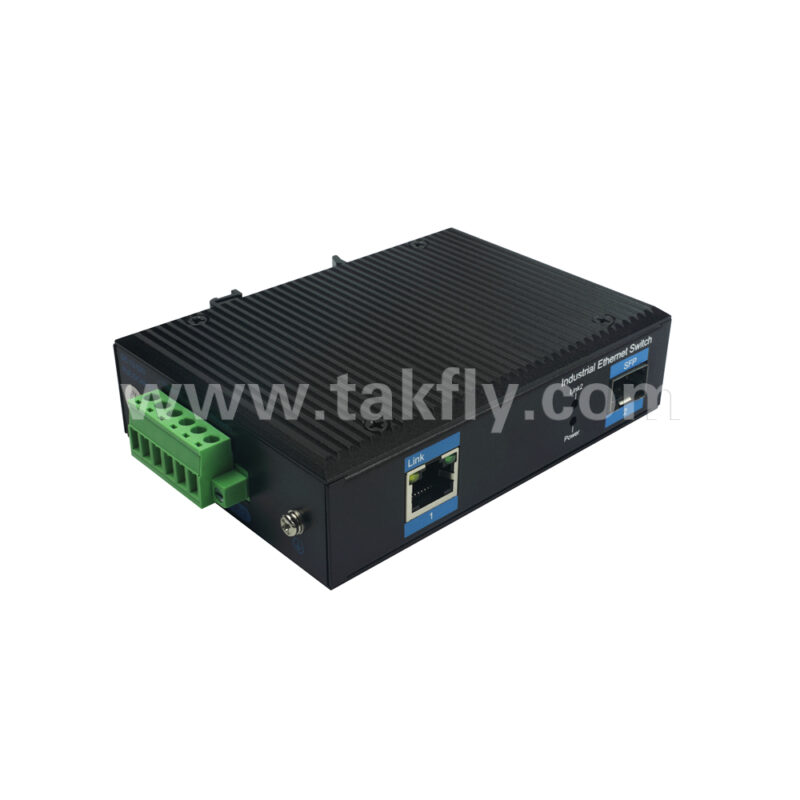
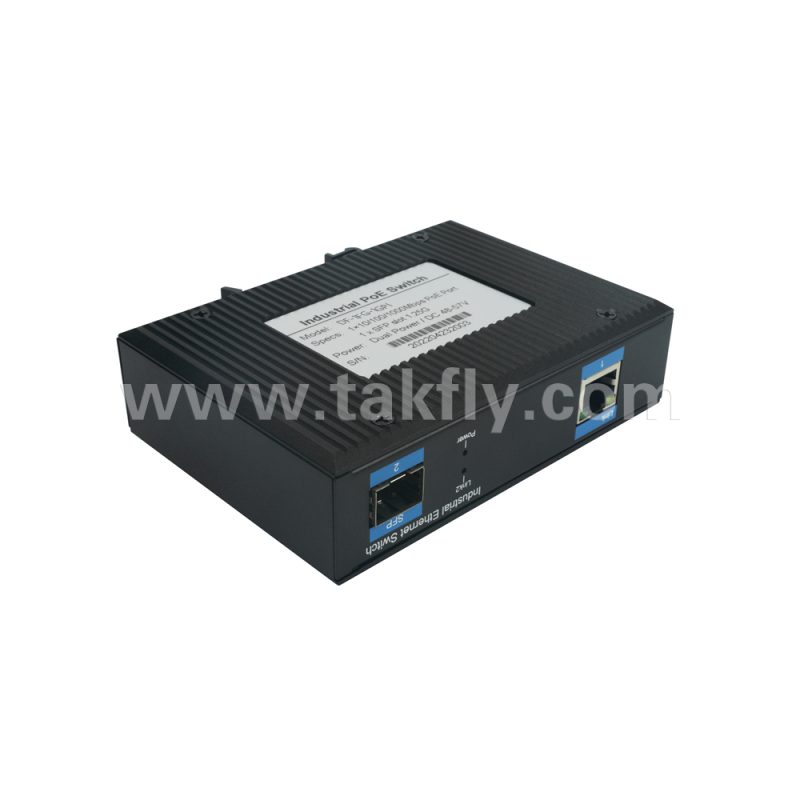
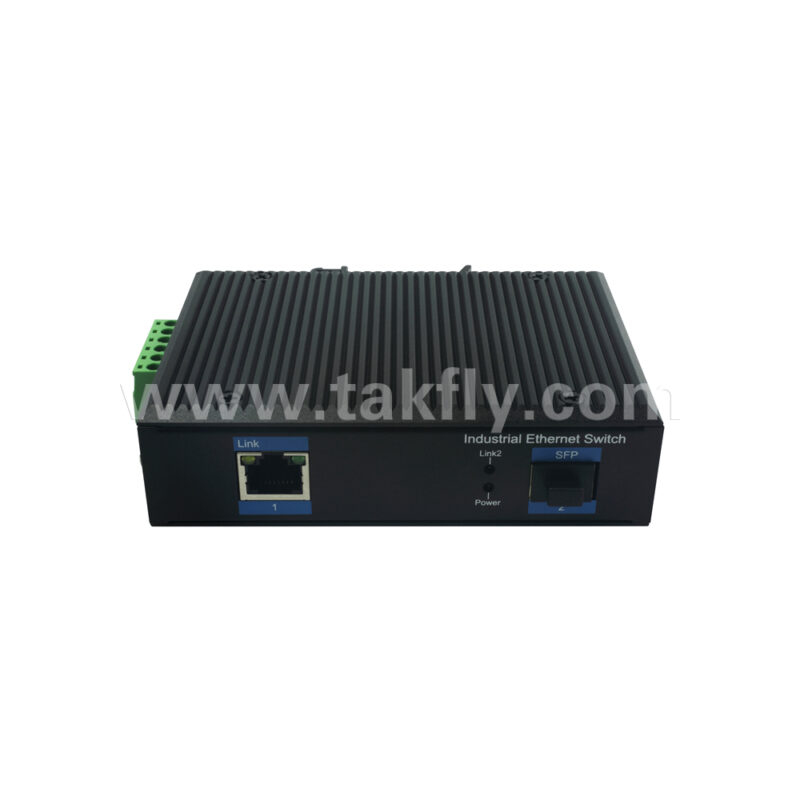
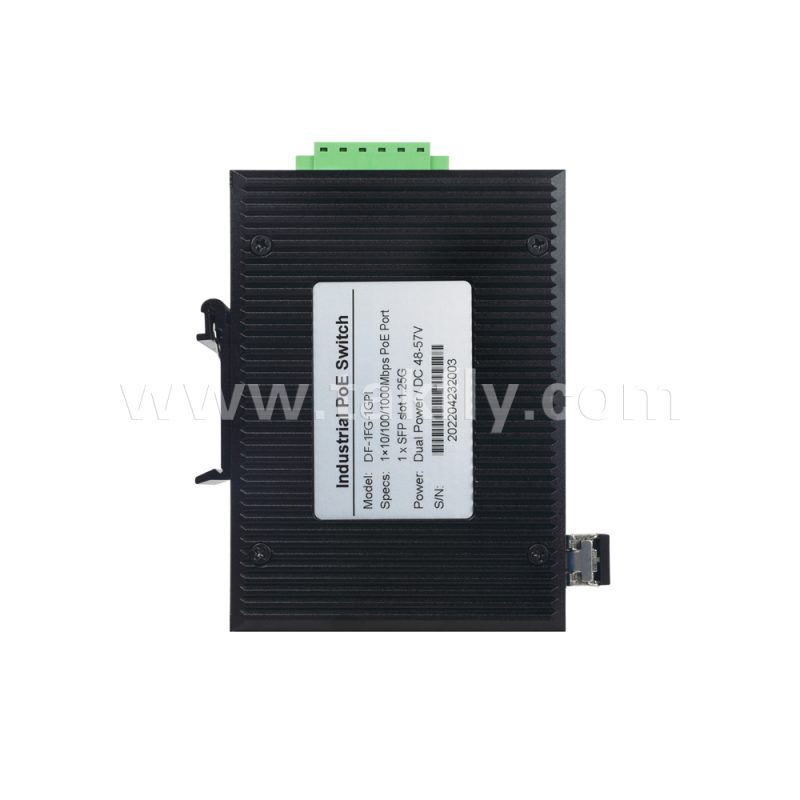
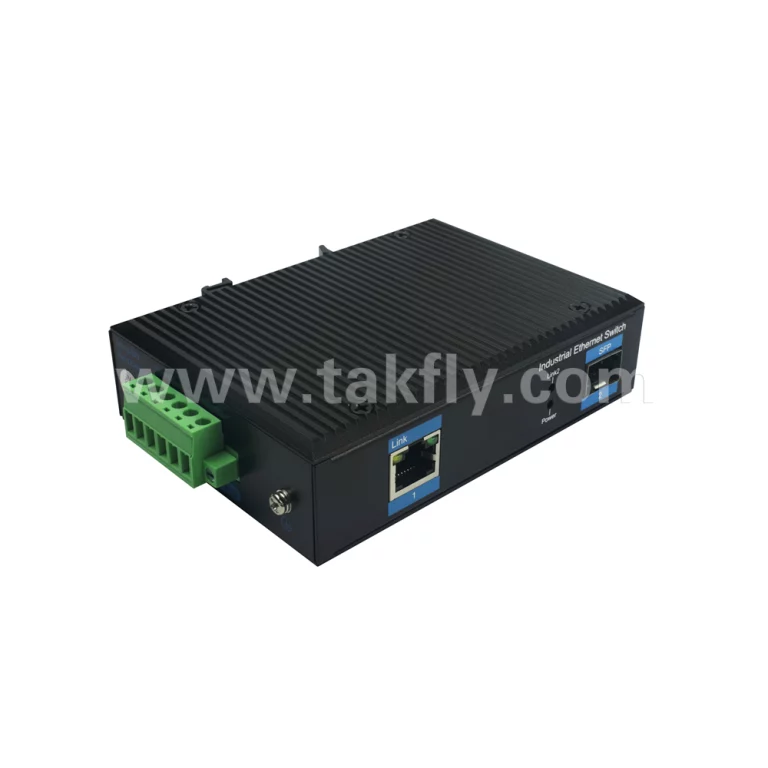
c. Rich expandability: Equipped with 1 x 1000Mbps SFP port fiber switch, users can flexibly choose fiber modules to achieve remote data transmission and meet various networking requirements.
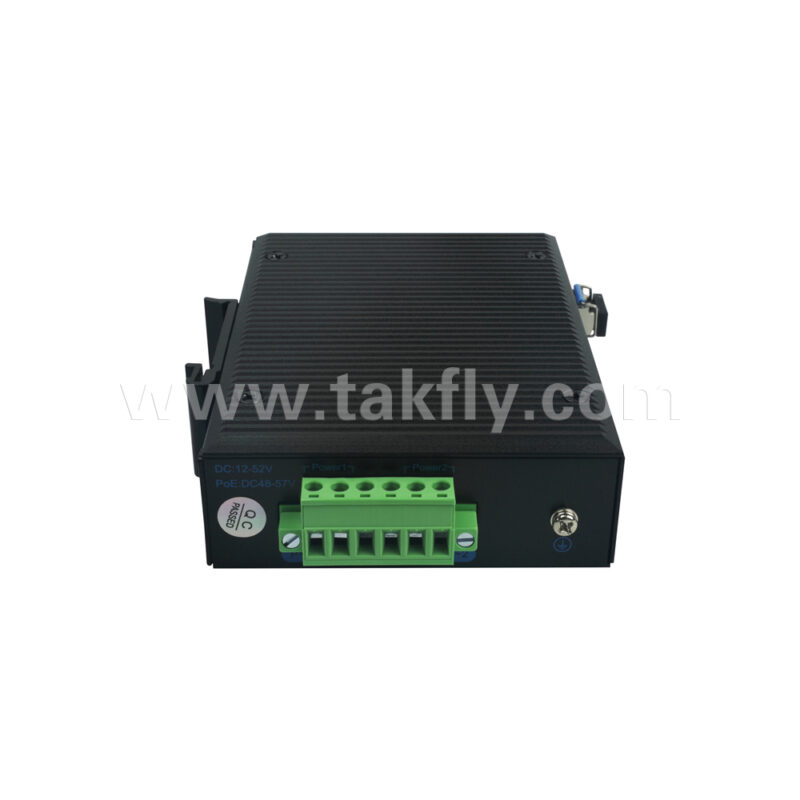
d. Industrial-grade design: The SFP fiber switch features a sturdy metal casing with excellent anti-interference performance and heat dissipation capabilities, making it suitable for harsh industrial environments such as high temperatures, humidity, and vibrations.
e. Simple and easy-to-use: The switch supports remote management and monitoring, facilitating network maintenance.
Additionally, it offers comprehensive fault diagnosis and alarm functions to help quickly identify and resolve issues.
Empowering Networks: Unveiling the Differences between POE and Traditional Ethernet Ports
As network devices become increasingly prevalent, the distinctions between Power over Ethernet (POE) and traditional Ethernet ports have emerged as a focal point of attention for many.
1 x 10/100/1000Mbps Industrial PoE Port + SFP Fiber Switch is worth purchasing.
What exactly is a POE port, and how does it differ from a traditional one?
1. An Introduction to POE Ports
POE ports, or Power over Ethernet ports, are interfaces that enable network cables to transmit both data and power to devices.
Originally standardized by the IEEE 802.3af standard, higher-power versions such as IEEE 802.3at and IEEE 802.3bt have since been developed.
POE ports allow devices to receive data and power simultaneously through a single cable, eliminating the need for additional power adapters.
2. Differences between POE and Traditional Ethernet Ports
1.Power Supply Method: Traditional Ethernet ports rely on external power adapters, while POE ports supply power through network cables.
This simplifies power supply lines, reduces device costs, and enhances deployment convenience.
2. Power Efficiency: Compared to traditional ports, POE ports offer higher efficiency. Depending on the standard, POE ports can provide power levels ranging from 5W, 15W, 30W, and even higher, sufficient for most network device requirements.
3. Compatibility: Not all network devices support POE functionality. While many switches, routers, and wireless access points offer POE capabilities, some lower-end devices still require traditional power adapters.
4. Safety: Since POE ports transmit electricity, safety is of paramount importance. POE devices should incorporate overvoltage protection, short-circuit protection, and other protective measures to ensure safety.
In conclusion:
POE and traditional Ethernet ports differ significantly in terms of power supply, efficiency, compatibility, and safety.
As network technology advances, POE’s convenience, efficiency, and safety make it an ideal choice for various network devices.
Understanding the differences between POE and traditional Ethernet ports helps consumers select suitable network devices for their needs.